.NET Interview Questions & Answers
What is the .NET?
.NET framework is supports an object-oriented approach, that provides an environment to run, debug and deploy code onto web services and applications
by using tools and functionalities like libraries, classes, and APIs.
What are the main components of .NET?
Following are the components of .NET
- Common Language run-time
- Application Domain
- Common Type System
- .NET Class Library
- .NET Framework
- Profiling
What do you know about CTS?
CTS stands for Common Type System.It follows certain rules according to which a data type should be declared and used in the program code. CTS also describes the data types that are going to be used in the application. We can even make our own classes and functions following the rules in the CTS, it helps in calling the data type declared in one program language by other programming languages.
What is CLR?
CLR stands for common language run-time, it is an important component of the .NET framework. We can use CLR as a building block of various applications and provides a secure execution environment for applications.
Whenever an application written in C# is compiled, the code is converted into an intermediate language. After this, the code is targeted to CLR which then performs several operations like memory management, security checks, loading assemblies, and thread management.
Explain CLS?
Common language specification helps the developers to use the components that are inter-language compatible with certain rules that come with CLS. It then helps in reusing the code in other .NET compatible languages.
What do you know about JIT?
JIT is a compiler which stands for Just In Time. It is used to convert the intermediate code into the native language. During the execution, the intermediate code is converted into the native language.
Why do we use Response.Output.Write()?
Response.Output.Write() is used to get the formatted output.
What is the difference between Response.Redirect and Server.Transfer?
Response.Redirect basically redirects the user’s browser to another page or site. The history of the user’s browser is updated to reflect the new address as well. It also performs a trip back to the client where the client’s browser is redirected to the new page.
Whereas, Server.Transfer transfers from one page to the other without making any round-trip back to the client’s browser. The history does not get updated in the case of Server.Transfer.
What is the difference between managed and unmanaged code?
Managed code runs inside CLR and installing the .NET Framework is necessary to execute it. Unmanaged code does not depend on CLR for execution and is developed using languages outside the .NET framework.
| Managed code |
Unmanaged code |
| Managed code is managed by CLR |
Any code that is not managed by CLR |
| .NET framework is necessary to execute managed code |
Independent of .NET framework |
| CLR manages memory management through garbage collection |
Own runtime environment for compilation and execution |
Explain the difference between a class and an object?
Class is a Logical Unit or Blueprint. It contains fields, methods, and properties.
An object is an instance of a class.
What is difference between Boxing and Unboxing?
| Boxing |
Unboxing |
| Boxing is a process of converting value type to reference type. |
Unboxing is a process of converting reference type to value type. |
| Implicit |
Explicit |
Differentiate between constants and read-only variables.
| Constants |
Read-only Variables |
| Evaluated at compile time |
Evaluated at run-time |
| Support only value type variables |
They can hold the reference type variables |
| They are used when the value is not changing at compile time |
Used when the actual value is unknown before the run-time |
| Cannot be initialized at the time of declaration or in a constructor |
Can be initialized at the time of declaration or in a constructor |
What is BCL?
- BCL is a base class library of classes, interfaces and value types
- It is the foundation of .NET framework applications, components, and controls
- Encapsulates a huge number of common functions and make them easily available for the developers
- It provides functionality like threading, input/output, security, diagnostics, resources, globalization, etc.
- Also serves the purpose of interaction between user and runtime
- It also provides namespaces that are used very frequently. for eg: system, system.Activities, etc.
What is the difference between namespace and assembly?
An assembly is a physical grouping of logical units whereas namespace groups classes. Also, a namespace can span multiple assemblies as well.
What is LINQ?
LINQ (Language Integrated Query) is a feature of the .NET framework that allows developers to write queries for different types of data sources directly in C# or VB.NET. It was introduced with .NET Framework 3.5. LINQ provides a consistent, readable, and compact syntax for querying data, whether it's in-memory collections like arrays and lists, databases, XML documents, or even more exotic data sources. Here are some key aspects of LINQ:
What is MSIL?
MSIL (Microsoft Intermediate Language), also known as CIL (Common Intermediate Language), is a language used by the .NET Framework. It is an intermediate code that .NET compilers convert source code into, regardless of the programming language used. MSIL is then compiled into native machine code at runtime by the .NET Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler, enabling applications to run on any hardware platform supported by .NET. This process ensures platform independence and facilitates interoperability among different .NET languages.
Explain the different parts of the assembly.
Following are the different parts of assembly:
- Manifest: It has the information about the version of the assembly.
- Type Metadata: Contains the binary information of the program
- MSIL: Microsoft Intermediate Language Code
- Resources: List of related files
How do you prevent a class from being inherited?
Use the sealed keyword to prevent a class from being inherited.
What are the different types of constructors in c#?
- Default Constructor
- Parameterized constructor
- Copy Constructor
- Static Constructor
- Private Constructor
What are the different types of assemblies?
- Private Assembly: It is accessible only to the application, it is installed in the installation directory of the application.
- Shared Assembly: It can be shared by multiple applications, it is installed in the GAC.
What are MDI and SDI?
- MDI( Multiple Document Interface): An MDI lets you open multiple windows, it will have one parent window and as many child windows. The components are shared from the parent window like menubar, toolbar, etc.
- SDI( Single Document Interface): It opens each document in a separate window. Each window has its own components like menubar, toolbar, etc. Therefore it is not constrained to the parent window.
What is the difference between custom and user control?
| Custom Control |
User Control |
| Derives from control |
Derives from UserControl |
| Dynamic Layout |
Static Layout |
| Defines a single control |
Defines a set of con |
| It has full toolbox support |
Cannot be added to the toolbox |
| Loosely coupled control |
Tightly coupled control |
What is a garbage collector?
In .NET, the garbage collector (GC) is an automatic memory management system that helps manage the allocation and release of memory in your applications. The .NET garbage collector operates by periodically identifying .NET objects in the managed heap that are no longer being used by the application, deallocating their memory, and making it available again. This process prevents memory leaks and optimizes the application's memory usage, contributing to system stability and performance. The GC in .NET is generational, meaning it organizes objects into generations that assume objects that have survived previous collections are less likely to need to be collected. This optimizes the GC process, making it faster and more efficient.
What is caching?
Caching simply means storing the data temporarily in the memory so that the data can be accessed from the memory instead of searching for it in the original location. It increases the efficiency of the application and also increases its speed.
- Page caching
- Data caching
- Fragment caching
What is .Net Reflection?
Reflection objects are used for creating type instances and obtaining type information at runtime. The classes in the System.Reflection namespace gives access to the metadata of a running program.
What is Object-Role Modeling (ORM)?
Object-Role Modeling (ORM) is a powerful method for designing and querying information systems at the conceptual level. It is an easy and understandable description of the application for non-technical users.
What are globalization and localization?
Globalization is designing and coding culture-neutral and language-neutral applications. Localization is customizing the application and translating the UI based on specific cultures and regions.
What is MIME?
MIME stands for Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension. It is an add-on or a supplementary protocol that allows non-ASCII data to be sent through SMTP. It facilitates the exchange of data files on the internet and was proposed by Bell Communications in 1991.
What is a Hashtable?
The Hashtable class is a collection that stores key-value pairs. It organizes the pairs based on the hash code of each key and uses it to access elements in the collection.
What are the design principles used in .NET?
Net uses the SOLID design principle which includes the following:
- Single responsibility principle (SRP)
- Open-Closed Principle (OCP)
- Liskov substitution principle (LSP)
- Interface segregation principle (ISP)
- Dependency inversion principle (DIP)
What is Marshaling?
Marshaling is the process of transforming types in the managed and unmanaged code.
What are the divisions of the Memory Heap?
The memory heap is divided into three generations.
- Generation 0: Used to store short-lived objects. Frequent Garbage Collection happens in this Generation.
- Generation 1: Used for medium-lived objects.
- Generation 2: Used for long-lived objects.
Differentiate between a Debug build and a Release build?
Debug builds do not optimize and allow the accurate setting of breakpoints. They contain debugging symbols, but the code built-in "Release" mode is optimized for speed or size without any debug data.
What is the application object?
The Application object is used to share information among all users of an application. You can tie a group of ASP files that work together to perform some purpose.
What is the session object?
A Session object stores information and variables about a user and retains it through the session.
How is a Managed code executed?
- Choose a language compiler depending on the language of the code.
- Convert the code into Intermediate language using its own compiler.
- The IL is then targeted to CLR which converts the code into native code using JIT.
- Execution of Native code.
What is MVC?
MVC stands for model view controller which is an architecture to build .NET applications.
Model: They are the logical part of any application that handles the object storage and retrieval from the databases for an application.
View: View handles the UI part of an application. They get the information from the models for their display.
Controller: They handle the user interactions, figure out the responses for the user input and also render the view that is required for the user interaction.
What is a .NET web service?
It is a component that allows the publishing of the application's function on the web to make it accessible to the public. It resides on a Web server and provides information and services using standard Web protocols such as HTTP and Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP).
What are the advantages of Web Services?
- It is simple to build and supported by a variety of platforms.
- It can extend its interface and add new methods without affecting the client's operations.
- It is stateless and firewall-friendly.
What is CAS?
CAS stands for code access security, CAS is a part of a security model that prevents unauthorized access to the resources. It also enables the users to set permissions for the code. CLR then executes the code depending upon the permissions.
CAS can only be used for managed code. If an assembly uses CAS it is treated as partially trusted. Although it goes through checks each time an assembly tries to access the resources.
What is MEF?
MEF stands for Managed Extensibility Framework. It is a library that allows the host application to consume external extensions without any configuration requirement.
What are Tuples?
Tuples are data structures that hold object properties and contain a sequence of elements of different data types. They were introduced as a Tuple class in .NET Framework 4.0 to avoid the need of creating separate types to hold object properties.
What is the application domain?
ASP.NET introduces a concept of application domain or AppDomain which is like a lightweight process that acts like both container and boundary. The .NET run-time uses the AppDomain as a container for data and code. The CLR allows multiple .NET applications to run in a single AppDomain.
What is delegate in .NET?
A delegate in .NET is similar to a function pointer in other programming languages like C or C++. A delegate allows the user to encapsulate the reference of a method in a delegate object. A delegate object can then be passed in a program, which will call the referenced method. We can even use a delegate method to create a custom event in a class.
Difference between interface and abstract class in .NET?
Interface
- An interface merely declares a contract or behavior that implementing classes should have.
- An interface may declare only properties, methods and events with no access modifier.
Abstract Class
- An abstract class provides a partial implementation for a functionality that must be implemented by the inheriting entities.
- An abstract class declares fields too.
Neither interface nor an abstract class can be instantiated.
What is the difference between a stack and a heap?
Stack
- Stored value type
- A stack is responsible for keeping track of each executing thread and its location.
Heap
- Stored reference type
- The heap is responsible for keeping track of the more precise objects or data.
What are the different validators in ASP.NET?
- Client-side validation – When the validation takes place on the client-side browser, it is called client-side validation. Usually, JavaScript is used for client-side validation.
- Server-side validation – When the validation takes place on the server then it is called server-side validation. Server-side validation is considered as a secure form of validation because even if the user bypasses the client-side validation we can still catch it in server-side validation.
What are EXE and DLL?
EXE and DLL are assembly executable modules.
- EXE: It is an executable file that runs the application for which it is designed. When we build an application, an exe file is generated. Therefore the assemblies are loaded directly when we run an exe. But an exe file cannot be shared with other applications.
- DLL: It stands for dynamic link library that consists of code that needs to be hidden. The code is encapsulated in this library, an application can have many DLLs and can also be shared with other applications.
List the events in the page life cycle.
Following are the events in the page life cycle:
- Page Request: The page request initiates the life cycle. If the page is not yet in memory, it's created and initialized.
- Start: This event signals the start of page initialization. At this point, the page properties such as Request and Response are set.
- Initialization: During this stage, controls on the page are initialized, including loading view state data, if any.
- Load: The Load event is raised for all controls on the page recursively. At this stage, the page is fully initialized, and any postback data has been processed.
- Postback Event Handling: If the request is a postback, the related event handlers are executed. This includes events such as button clicks or dropdown selections.
- Rendering: The page calls the Render method for each control, providing a text-based output that represents the control's UI.
- Unload: Once the page has been fully rendered, the Unload event is raised for all controls. This allows for cleanup tasks and finalization before the page is disposed.
What are the event handlers that we have for the Global.asax file?
Application Events:
- Application_Start, Application_End, Application_AcquireRequestState,
Application_AuthenticateRequest, Application_AuthorizeRequest,
Application_BeginRequest, Application_Disposed, Application_EndRequest,
Application_Error, Application_PostRequestHandlerExecute,
Application_PreRequestHandlerExecute, Application_PreSendRequestContent,
Application_PreSendRequestHeaders, Application_ReleaseRequestState,
Application_ResolveRequestCache, Application_UpdateRequestCache
Session Events:
- Session_Start, Session_End
Explain role-based security?
Role-based security is used to implement security measures based on the role assigned to the users in the organization. Then we can authorize users based on their roles in the organization. For example, windows have role-based access like user, administrators, and guests.
What is cross-page posting?
Whenever we click on a submit button on a page, the data is stored on the same page. But if the data is stored on a different page, it is known as a cross-page posting.
Cross-page posting can be achieved by POSTBACKURL property which causes the postback.
FindControl method can be used to get the values that are posted on this page to which the page has been posted.
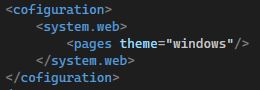
How can we apply themes to an ASP.NET application?
We can use the web.config file to specify the themes
Explain passport authentication.
During the passport authentication, it first checks the passport authentication cookie, if the cookie is not available the application redirects to the passport sign on page. Passport service then authenticates the details of the user on the sign on page and if they are valid, stores them on the client machine and then redirects the user to the requested page.
What are ASP.NET security controls?
- <asp:Login>: Provides a login capability that enables users to enter their credentials.
- <asp: LoginName>: Allows you to display the name of the logged-in user.
- <asp: LoginStatus>: Displays if the user is authenticated or not.
- <asp: LoginView>: provides various login views depending on the template that has been selected.
- <asp: PasswordRecovery>: Emails the users the lost passwords.
List all the templates of the Repeater control.
- ItemTemplate
- AlternatingItemTemplate
- SeparatorTemplate
- HeaderTemplate
- FooterTemplate
What is the appSettings section in the web.config file?
If we want to set the user-defined values for the whole applications, we can use the appSettings block in the web.config file. For example the code below uses the ConnectionString throughout the project for the database connection:
<em>
<configuration>
<appsettings>
<add key= "ConnectionString" value="server=local; pwd=password; database=default" />
</appSettings>
</configuration>
</em>
What is HTTP Handler?
Every request into an ASP.NET application is handled by a specialized component called HTTP handler. It is the most important component for handling ASP.NET application requests.
It uses different handlers to serve different files. The handler for web page creates the page and control objects, runs your code and then renders the final HTML.
Following are the default HTTP handlers for ASP.NET:
- Page Handler(.aspx): Handles web pages
- User Control Handler(.ascx): It handles web user control pages
- Web Service Handler(.asmx): Handles web service pages
- Trace Handler(trace.axd): It handles trace functionality
What are the different types of cookies in ASP.NET?
- Session Cookie: It resides on the client machine for a single session until the user logs out.
- Persistent Cookie: Resides on the user machine for a period specified for its expiry. It may be an hour, a month or never.
What is the difference between ExecuteScalar and ExecuteNonQuery?
| ExecuteScalar |
ExecuteNonQuery |
| Returns the output value |
Does not return any value |
| Used for fetching a single value |
Used to execute insert and update statements |
| Does not return the number of affected rows |
Returns the number of affected rows. |
What is ADO?
ADO stands for ActiveX Data Objects. It is an application program for writing Windows applications. It is used to get access to a relational or non-relational database from database providers such as Microsoft and others.
What are the fundamental objects in ADO.NET?
- DataReader: connected architecture.
- DataSet: disconnected architecture.
What is Object Pooling?
Object Pooling is a concept for optimal use of limited resources through software constructs. The ready-to-use objects, connections, and threads are stored in a pool (group) of objects in memory for later use. For creating a new object, it is pulled from the pool and allocated for the request. Pooling helps in improving performance and facilitates scalability.
What are client-side and server-side validations in Web pages?
Client-side validations take place at the client end with the help of JavaScript and VBScript offering a better user experience. The inputs for client-side validation are validated in the user’s browser. While, server-side validations take place at the server end using ASP.Net and PHP, and the feedback is sent through a dynamically generated new webpage.
What is Serialization?
Serialization is the process of converting the state of an object into a form (a stream of bytes) to be persisted or transported. Deserialization converts a stream into an object and is the opposite of serialization. These processes allow data to be stored and transferred.
What is a PE file?
PE stands for Portable Executable. It is a derivative of the Microsoft Common Object File Format (COFF). Windows executable. EXE or DLL files follow the PE file format. It consists of four parts:
- PE/COFF headers: Contains information regarding. EXE or DLL file.
- CLR header: Contains information about CLR & memory management.
- CLR data: Contains metadata of DDLs and MSIL code generated by compilers.
- Native image section: Contains sections like .data, .rdata, .rsrc, .text etc.
What is the difference between DLL and EXE?
.EXE files are single outbound files that cannot be shared with other applications. DLL files are multiple inbound files that are shareable.
What is the difference between dataset.clone and dataset. copy?
Dataset.clone copies only the structure of the DataSet which includes all DataTable schemas, relations, and constraints but it does not copy any data. Dataset. copy is a deep copy of the DataSet that duplicates both its structure and data.
Describe the use of ErrorProvider Control in .NET?
The ErrorProvider control is used to indicate invalid data or errors to the end-user while filling a data entry form. In case of invalid data entry, the error message attached to the error description string is displayed next to the control.
Differentiate between Task and Thread in .NET?
The thread represents an actual OS-level thread, with its own stack and kernel resources, and allows the highest degree of control. You can choose to Abort() or Suspend() or Resume() a thread, and set thread-level properties, like the stack size, apartment state, or culture. While a Task class from the Task Parallel Library is executed by a TaskScheduler to return a result and allows you to find out when it finishes.
What is Multithreading?
Multi-threading is a process that contains multiple threads each of which performs different activities within a single process. .NET supports multithreading in two ways:
- Starting threads with ThreadStart delegates.
- Using the ThreadPool class with asynchronous methods.